Trace with LangGraph (Python and JS/TS)
LangSmith smoothly integrates with LangGraph (Python and JS) to help you trace agentic workflows, whether you're using LangChain modules or other SDKs.
With LangChain
If you are using LangChain modules within LangGraph, you only need to set a few environment variables to enable tracing.
This guide will walk through a basic example. For more detailed information on configuration, see the Trace With LangChain guide.
0. Installation
Install the LangGraph library and the OpenAI integration for Python and JS (we use the OpenAI integration for the code snippets below).
For a full list of packages available, see the LangChain Python docs and LangChain JS docs.
- pip
- yarn
- npm
- pnpm
pip install langchain_openai langgraph
yarn add @langchain/openai @langchain/langgraph
npm install @langchain/openai @langchain/langgraph
pnpm add @langchain/openai @langchain/langgraph
1. Configure your environment
- Python
- TypeScript
export LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2=true
export LANGCHAIN_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
# The below examples use the OpenAI API, though it's not necessary in general
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
export LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2=true
export LANGCHAIN_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
# The below examples use the OpenAI API, though it's not necessary in general
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
If you are using LangChain.js with LangSmith and are not in a serverless environment, we also recommend setting the following explicitly to reduce latency:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=true
If you are in a serverless environment, we recommend setting the reverse to allow tracing to finish before your function ends:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=false
See this LangChain.js guide for more information.
2. Log a trace
Once you've set up your environment, you can call LangChain runnables as normal. LangSmith will infer the proper tracing config:
- Python
- TypeScript
from typing import Literal
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
@tool
def search(query: str):
"""Call to surf the web."""
if "sf" in query.lower() or "san francisco" in query.lower():
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy."
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny."
tools = [search]
tool_node = ToolNode(tools)
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0).bind_tools(tools)
def should_continue(state: MessagesState) -> Literal["tools", "__end__"]:
messages = state['messages']
last_message = messages[-1]
if last_message.tool_calls:
return "tools"
return "__end__"
def call_model(state: MessagesState):
messages = state['messages']
# Invoking `model` will automatically infer the correct tracing context
response = model.invoke(messages)
return {"messages": [response]}
workflow = StateGraph(MessagesState)
workflow.add_node("agent", call_model)
workflow.add_node("tools", tool_node)
workflow.add_edge("__start__", "agent")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"agent",
should_continue,
)
workflow.add_edge("tools", 'agent')
app = workflow.compile()
final_state = app.invoke(
{"messages": [HumanMessage(content="what is the weather in sf")]},
config={"configurable": {"thread_id": 42}}
)
final_state["messages"][-1].content
import { HumanMessage, AIMessage } from "@langchain/core/messages";
import { tool } from "@langchain/core/tools";
import { z } from "zod";
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { StateGraph, StateGraphArgs } from "@langchain/langgraph";
import { ToolNode } from "@langchain/langgraph/prebuilt";
interface AgentState {
messages: HumanMessage[];
}
const graphState: StateGraphArgs<AgentState>["channels"] = {
messages: {
reducer: (x: HumanMessage[], y: HumanMessage[]) => x.concat(y),
},
};
const searchTool = tool(async ({ query }: { query: string }) => {
if (query.toLowerCase().includes("sf") || query.toLowerCase().includes("san francisco")) {
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy."
}
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny."
}, {
name: "search",
description:
"Call to surf the web.",
schema: z.object({
query: z.string().describe("The query to use in your search."),
}),
});
const tools = [searchTool];
const toolNode = new ToolNode<AgentState>(tools);
const model = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 0,
}).bindTools(tools);
function shouldContinue(state: AgentState) {
const messages = state.messages;
const lastMessage = messages[messages.length - 1] as AIMessage;
if (lastMessage.tool_calls?.length) {
return "tools";
}
return "__end__";
}
async function callModel(state: AgentState) {
const messages = state.messages;
// Invoking `model` will automatically infer the correct tracing context
const response = await model.invoke(messages);
return { messages: [response] };
}
const workflow = new StateGraph<AgentState>({ channels: graphState })
.addNode("agent", callModel)
.addNode("tools", toolNode)
.addEdge("__start__", "agent")
.addConditionalEdges("agent", shouldContinue)
.addEdge("tools", "agent");
const app = workflow.compile();
const finalState = await app.invoke(
{ messages: [new HumanMessage("what is the weather in sf")] },
{ configurable: { thread_id: "42" } }
);
finalState.messages[finalState.messages.length - 1].content;
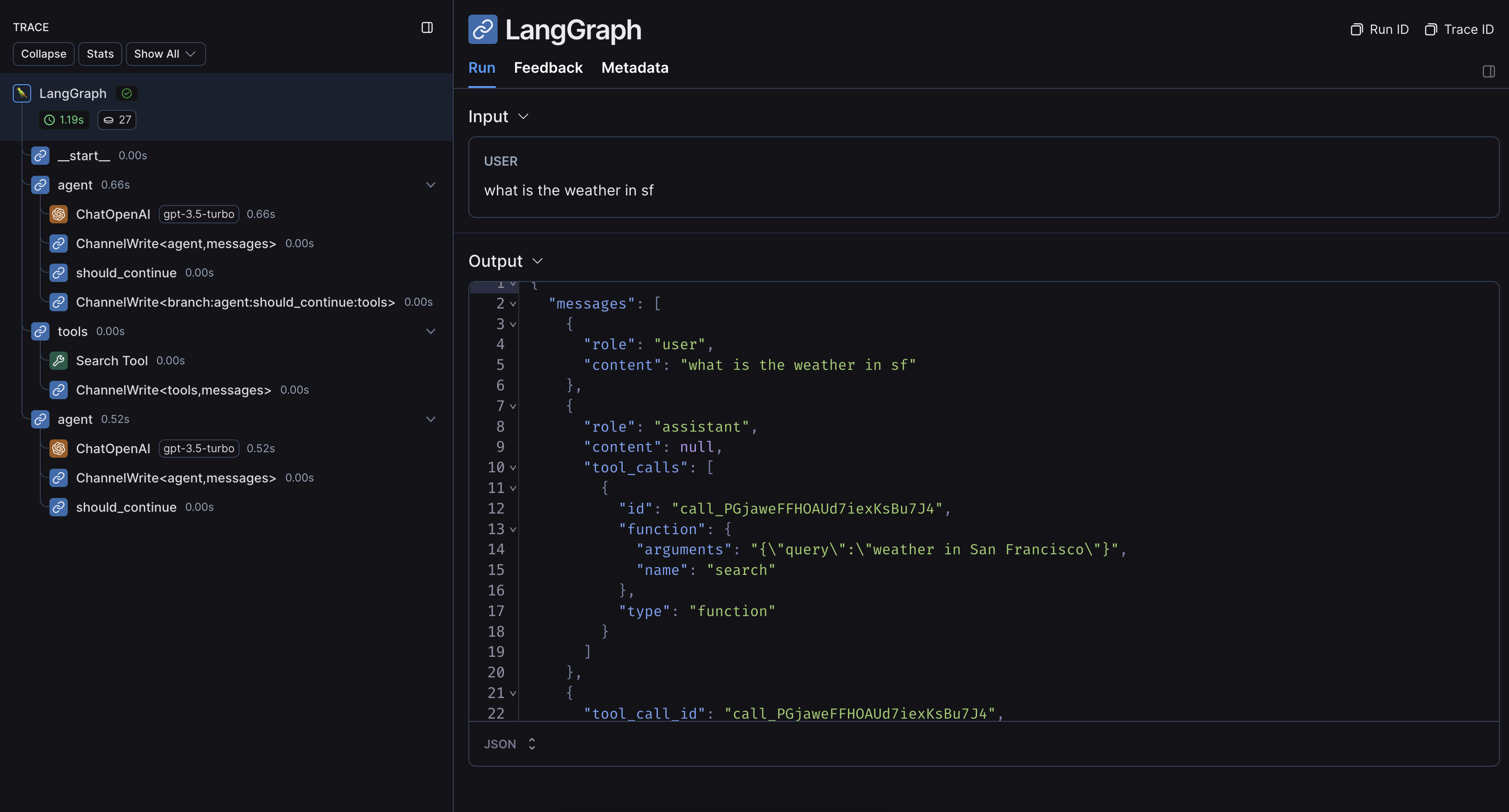
An example trace from running the above code looks like this:
Without LangChain
If you are using other SDKs or custom functions within LangGraph, you will need to wrap or decorate them appropriately
(with the @traceable decorator in Python or the traceable function in JS, or something like e.g. wrap_openai for SDKs).
If you do so, LangSmith will automatically nest traces from those wrapped methods.
Here's an example. You can also see this page for more information.
0. Installation
Install the LangGraph library and the OpenAI SDK for Python and JS (we use the OpenAI integration for the code snippets below).
- pip
- yarn
- npm
- pnpm
pip install openai langsmith langgraph
yarn add openai langsmith @langchain/langgraph
npm install openai langsmith @langchain/langgraph
pnpm add openai langsmith @langchain/langgraph
1. Configure your environment
- Python
- TypeScript
export LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2=true
export LANGCHAIN_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
# The below examples use the OpenAI API, though it's not necessary in general
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
export LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2=true
export LANGCHAIN_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
# The below examples use the OpenAI API, though it's not necessary in general
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
If you are using LangChain.js with LangSmith and are not in a serverless environment, we also recommend setting the following explicitly to reduce latency:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=true
If you are in a serverless environment, we recommend setting the reverse to allow tracing to finish before your function ends:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=false
See this LangChain.js guide for more information.
2. Log a trace
Once you've set up your environment, wrap or decorate the custom functions/SDKs you want to trace. LangSmith will then infer the proper tracing config:
- Python
- TypeScript
import json
import openai
import operator
from langsmith import traceable
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
from typing import Annotated, Literal, TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, operator.add]
tool_schema = {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "search",
"description": "Call to surf the web.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"query": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["query"],
},
},
}
# Decorating the tool function will automatically trace it with the correct context
@traceable(run_type="tool", name="Search Tool")
def search(query: str):
"""Call to surf the web."""
if "sf" in query.lower() or "san francisco" in query.lower():
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy."
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny."
tools = [search]
def call_tools(state):
function_name_to_function = {"search": search}
messages = state["messages"]
tool_call = messages[-1]["tool_calls"][0]
function_name = tool_call["function"]["name"]
function_arguments = tool_call["function"]["arguments"]
arguments = json.loads(function_arguments)
function_response = function_name_to_function[function_name](**arguments)
tool_message = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call["id"],
"role": "tool",
"name": function_name,
"content": function_response,
}
return {"messages": [tool_message]}
wrapped_client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
def should_continue(state: State) -> Literal["tools", "__end__"]:
messages = state["messages"]
last_message = messages[-1]
if last_message["tool_calls"]:
return "tools"
return "__end__"
def call_model(state: State):
messages = state["messages"]
# Calling the wrapped client will automatically infer the correct tracing context
response = wrapped_client.chat.completions.create(
messages=messages, model="gpt-3.5-turbo", tools=[tool_schema]
)
raw_tool_calls = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls
tool_calls = [tool_call.to_dict() for tool_call in raw_tool_calls] if raw_tool_calls else []
response_message = {
"role": "assistant",
"content": response.choices[0].message.content,
"tool_calls": tool_calls,
}
return {"messages": [response_message]}
workflow = StateGraph(State)
workflow.add_node("agent", call_model)
workflow.add_node("tools", call_tools)
workflow.add_edge("__start__", "agent")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"agent",
should_continue,
)
workflow.add_edge("tools", 'agent')
app = workflow.compile()
final_state = app.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what is the weather in sf"}]}
)
final_state["messages"][-1]["content"]
Note: The below example requires langsmith>=0.1.39 and @langchain/langgraph>=0.0.31
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { StateGraph } from "@langchain/langgraph";
import { wrapOpenAI } from "langsmith/wrappers/openai";
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
type GraphState = {
messages: OpenAI.ChatCompletionMessageParam[];
};
const wrappedClient = wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI({}));
const toolSchema: OpenAI.ChatCompletionTool = {
type: "function",
function: {
name: "search",
description: "Use this tool to query the web.",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
query: {
type: "string",
},
},
required: ["query"],
}
}
};
// Wrapping the tool function will automatically trace it with the correct context
const search = traceable(async ({ query }: { query: string }) => {
if (
query.toLowerCase().includes("sf") ||
query.toLowerCase().includes("san francisco")
) {
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy.";
}
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny."
}, { run_type: "tool", name: "Search Tool" });
const callTools = async ({ messages }: GraphState) => {
const mostRecentMessage = messages[messages.length - 1];
const toolCalls = (mostRecentMessage as OpenAI.ChatCompletionAssistantMessageParam).tool_calls;
if (toolCalls === undefined || toolCalls.length === 0) {
throw new Error("No tool calls passed to node.");
}
const toolNameMap = {
search,
};
const functionName = toolCalls[0].function.name;
const functionArguments = JSON.parse(toolCalls[0].function.arguments);
const response = await toolNameMap[functionName](functionArguments);
const toolMessage = {
tool_call_id: toolCalls[0].id,
role: "tool",
name: functionName,
content: response,
}
return { messages: [toolMessage] };
}
const callModel = async ({ messages }: GraphState) => {
// Calling the wrapped client will automatically infer the correct tracing context
const response = await wrappedClient.chat.completions.create({
messages,
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
tools: [toolSchema],
});
const responseMessage = {
role: "assistant",
content: response.choices[0].message.content,
tool_calls: response.choices[0].message.tool_calls ?? [],
};
return { messages: [responseMessage] };
}
const shouldContinue = ({ messages }: GraphState) => {
const lastMessage =
messages[messages.length - 1] as OpenAI.ChatCompletionAssistantMessageParam;
if (
lastMessage?.tool_calls !== undefined &&
lastMessage?.tool_calls.length > 0
) {
return "tools";
}
return "__end__";
}
const workflow = new StateGraph<GraphState>({
channels: {
messages: {
reducer: (a: any, b: any) => a.concat(b),
}
}
});
const graph = workflow
.addNode("model", callModel)
.addNode("tools", callTools)
.addEdge("__start__", "model")
.addConditionalEdges("model", shouldContinue, {
tools: "tools",
__end__: "__end__",
})
.addEdge("tools", "model")
.compile();
await graph.invoke({
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "what is the weather in sf" }]
});
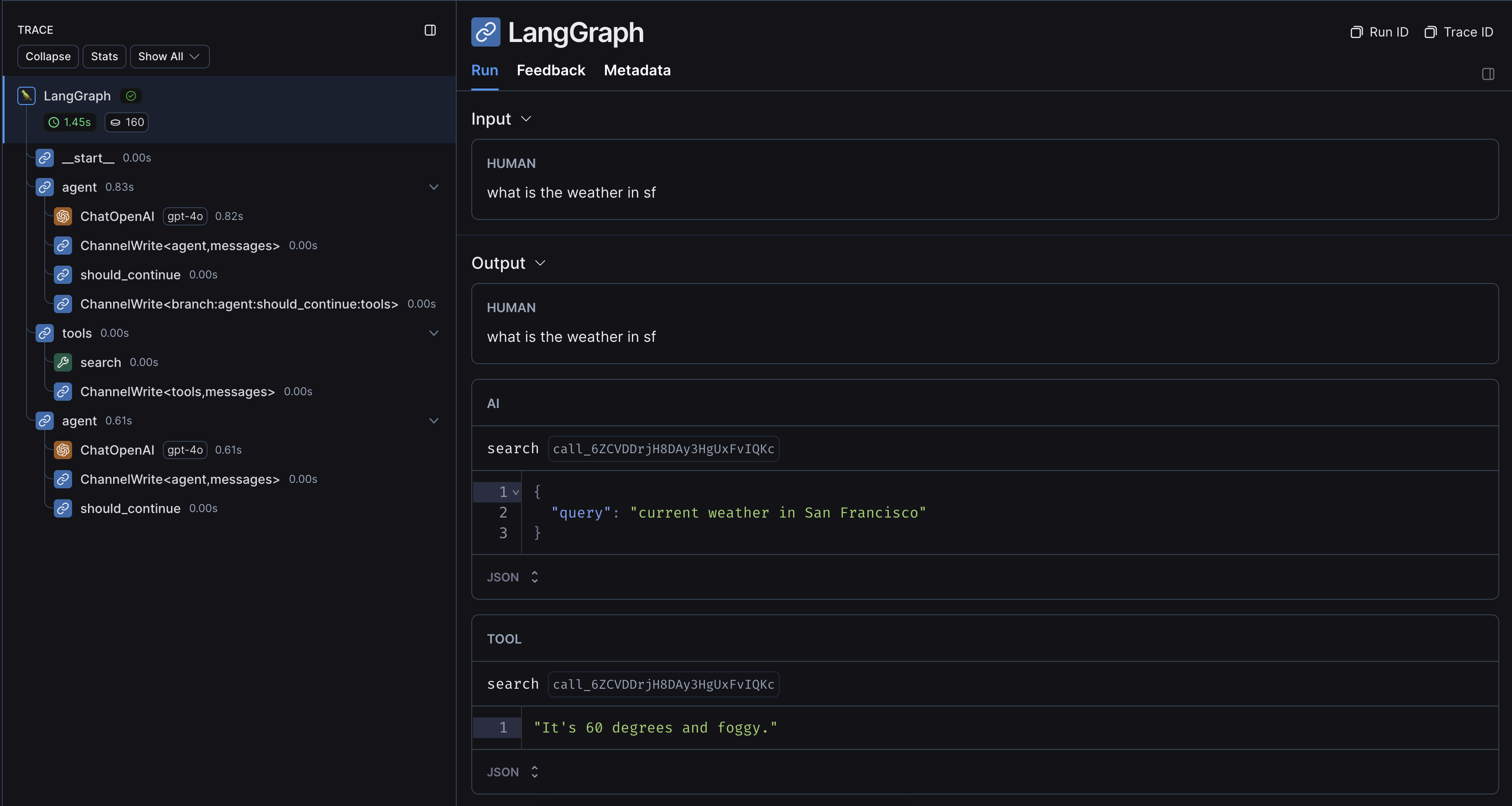
An example trace from running the above code looks like this: